Fluorescence microscopy
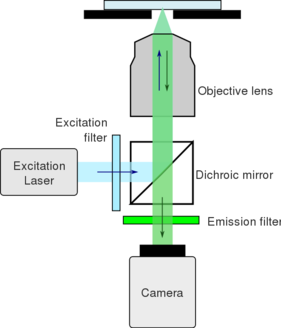
Fluorescence microscopy is an imaging tool which uses a high intensity light source to excite fluorescence in a sample of interest. Light is then emitted at a lower energy and is focused on a camera to form an image. Modern microscopes typically use a digital camera to form an image.
Components
Most microscopes contain the following components:
- Excitation light source - typically lasers or LEDs. These light sources are often connected to the microscope base by a fiber optic cable.
- Excitation filter - permits a narrow spectrum of light to pass through. Cleans up the excitation light.
- Dichroic mirror - reflects light of a particular range of spectra and allows the remainder of the light to pass through. This is used to filter the excitation light from the emitted fluorescence.
- Objective lens - focuses excitation light on the sample and collects the emitted fluorescence.
- Emission filter - permits a narrow spectrum of light to pass through. Cleans up the emitted light.
- Camera - Generates an image of the sample.
